Explore Policy Based Access Control (PBAC) frameworks, key inputs, effective strategies, results, and best practices for successful deployment in your organization.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, securing sensitive information and ensuring authorized access is more crucial than ever. Enter Policy Based Access Control (PBAC)—an innovative framework designed to enhance security by imposing rules that govern user access based on specific policies. Unlike traditional methods, PBAC offers a more dynamic and adaptable approach, allowing organizations to not only protect their data but also streamline user interactions with critical resources. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Policy Based Access Control framework, explore key inputs for successful implementation, and discuss effective strategies for development. By understanding the results of PBAC and adhering to best practices, businesses can significantly bolster their security posture while ensuring compliance and operational efficiency. Join us as we navigate through the essential components of PBAC and unlock its potential for your organization.
Understanding Policy Based Access Control Framework
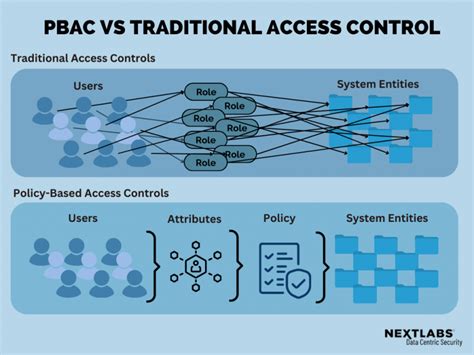
Policy based access control (PBAC) is a versatile and comprehensive approach to managing access within an organization. At its core, this framework establishes a clear set of guidelines and rules that dictate who can access specific resources and under what conditions. The emphasis on policies allows for dynamic management of permissions, making it an ideal solution in today’s rapidly changing environments.
The policy based access control framework is built upon several key principles:
- Granularity: Permissions can be customized at various levels, allowing organizations to define access controls that are as detailed or broad as necessary. This provides enhanced security and compliance.
- Flexibility: Policies can be adjusted dynamically based on changes in context, such as user roles, time, location, and more, adapting to the needs of the organization in real-time.
- Centralization: Management of access policies is centralized, making it easier to enforce changes and monitor compliance across the organization.
- Audibility: The framework supports logging and auditing of access events, which is essential for organizations to maintain oversight and accountability.
Implementing a proper policy based access control framework involves the following key components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Policy Definitions | Clearly outlined rules that dictate access permissions based on various attributes and context. |
| Access Control Lists (ACLs) | Lists that specify which users or groups can access specific resources and what actions they can perform. |
| Policy Enforcement Points (PEPs) | Systems or services that enforce access controls based on defined policies, ensuring compliance. |
By utilizing the policy based access control framework, organizations can not only enhance security but also improve operational efficiency, ultimately creating a more secure environment for their sensitive information.
Key Inputs for Implementing Policy Based Access Control
Implementing a successful policy based access control system requires several key inputs that, when aligned correctly, enhance security and operational efficiency. Below are the critical components to consider:
- Policy Definition: Clearly defined policies are essential. They dictate who has access to what resources, under what conditions. Policies should be concise, comprehensive, and easily understandable.
- User Roles and Attributes: Understanding the roles of users and their attributes (such as department, job function, or clearance level) is crucial for assigning access permissions. This aids in tailoring access rights based on specific job requirements.
- Resource Identification: Identify all resources within the organization—whether digital or physical—that require access control. This includes servers, databases, applications, and sensitive documents.
- Risk Assessment: Undertake a thorough risk assessment to understand vulnerabilities associated with each resource. This helps in determining the level of access control needed.
- Compliance Requirements: Be aware of regulatory compliance requirements that may affect access control policies. Compliance with standards (such as GDPR, HIPAA) should be integrated into policy formulation.
- Audit and Monitoring Framework: Establish a robust framework for auditing access control measures. It’s vital to continuously monitor and refine access based on user behavior and resource sensitivity.
- Training and Awareness: Employees should be trained on access control policies and the importance of adhering to them. Awareness can significantly reduce the risk of accidental policy breaches.
Collectively, these inputs create a strong foundation for effective policy based access control implementation, ensuring that security measures align with business objectives while maintaining ease of access for authorized users.
Development of Effective Policy Based Access Control Strategies
To successfully develop effective policy based access control strategies, organizations must take several critical steps that align their security needs with their operational objectives. Below are essential components of crafting a robust policy based access control framework.
1. Define Clear Access Policies
The first step in developing effective policy based access control strategies is to clearly define what the access policies should be. These policies should be based on the organization’s specific needs, compliance requirements, and potential risk factors. They must cover who can access what information and under which circumstances.
2. Assess Risk and Compliance Requirements
Organizations must conduct thorough risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and compliance requirements that shape their policy based access control framework. By understanding these elements, organizations can create policies that mitigate risks effectively while ensuring regulatory adherence.
3. Involve Stakeholders
Collaboration with stakeholders throughout the organization is crucial for ensuring that the developed policies meet the needs of different departments. Engaging with IT, HR, and legal departments provides a comprehensive view of the organization’s landscape and helps in refining access control policies.
4. Implement User Role Categorization
Establishing user roles is essential in defining the level of access each user should have. User roles can be derived from job functions, ensuring that employees only have access to the information necessary for their specific roles, which is a fundamental principle of policy based access control.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
After implementing policy based access control strategies, continuous monitoring and evaluation are necessary to ensure their effectiveness. Regular audits and assessments help identify policy gaps or areas that require adjustment based on evolving threats and organizational changes.
6. Incorporate Advanced Technologies
Utilizing advanced technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence can significantly enhance policy based access control. These technologies analyze user behavior and automatically adjust access rights, optimizing security without impeding productivity.
7. Train and Educate Employees
Comprehensive training on access control policies is vital for all employees. Ensuring that staff members understand the policies and the importance of adhering to them can reduce the likelihood of breaches due to human error.
8. Document Everything
Maintaining detailed documentation of all access controls, policies, and their rationale is critical. Documented procedures provide a reference point for training, audits, and compliance checks, thus ensuring transparency and accountability.
By following these steps, organizations can develop strong and effective policy based access control strategies that not only protect sensitive information but also support the organization’s overall objectives and compliance requirements.
Results of Implementing Policy Based Access Control Approaches
Implementing policy based access control approaches yields significant benefits that enhance security, streamline management, and foster compliance within organizations. Here are some key outcomes observed from such implementations:
The implementation of effective policy based access control approaches results in strengthened security, operational efficiency, and compliance facilitation, making it a crucial strategy for modern organizations.
Best Practices for Policy Based Access Control Deployment
Implementing policy based access control requires a structured approach to ensure security and efficiency. Here are some best practices to consider during deployment:
- Define Clear Policies: Establish straightforward, comprehensive policies that address who can access what resources under specific conditions. This clarity helps users understand their access rights.
- Utilize Roles Effectively: Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to streamline access rights assignment. By categorizing users into roles based on their job functions, you enhance the management of policy based access control.
- Regularly Review and Update Policies: Schedule periodic reviews of your access control policies to adapt to changes in organizational needs or compliance requirements. Outdated policies can lead to unnecessary security risks.
- Monitor Access Logs: Regularly analyze access logs to track and review who accessed what resources and when. This practice aids in identifying suspicious activities and enforcing accountability.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication: Enhance security by integrating multi-factor authentication (MFA) for accessing sensitive resources. This adds an additional layer of security beyond just usernames and passwords.
- Educate and Train Users: Conduct training sessions for end-users to ensure they understand the importance of policy based access control and can adhere to the security protocols in place.
- Test Policies Routinely: Regularly conduct tests and simulations to verify that access policies are functioning correctly and effectively mitigate security risks.
- Leverage Automation Tools: Use automation tools to manage and enforce access control policies, which can help streamline operations and reduce human error.
By incorporating these best practices, organizations can enhance their policy based access control framework and better protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC)?
Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC) is a security model that regulates access to resources based on policies defined by an organization. It allows for dynamic access control based on user attributes, resource requirements, and contextual information.
How does PBAC differ from traditional access control models?
Unlike traditional models such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), which assigns access based on predefined roles, PBAC is more flexible. It allows for real-time decision making based on a variety of factors including user identity, environment, and the specific resource being accessed.
What are the key components of a PBAC model?
The key components of a PBAC model include policies, policy decision points (PDP), policy enforcement points (PEP), and attributes. Policies define the conditions for access, while PDP assesses these conditions and PEP enforces the access decisions.
What are the benefits of implementing PBAC?
Benefits of implementing PBAC include enhanced security through fine-grained access control, improved compliance with regulations, and the ability to adapt quickly to changing access requirements and threats.
In what scenarios is PBAC most effective?
PBAC is most effective in complex environments where user attributes and contextual information are highly dynamic, such as in cloud services, multi-tenant architectures, and large organizations with diverse access needs.
Can PBAC work alongside other access control models?
Yes, PBAC can work alongside other access control models like RBAC and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC). Organizations often use a hybrid approach that combines multiple models for better security and flexibility.
What challenges might organizations face when adopting PBAC?
Challenges in adopting PBAC include the complexity of policy creation and management, the need for a robust infrastructure to support real-time analysis, and potential resistance to change among users accustomed to traditional access control methods.