In today’s digital landscape, ensuring robust security protocols is paramount for safeguarding sensitive information.
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) Systems provide a dynamic solution, allowing organizations to regulate who can access specific resources based on user identity and privileges. This article delves into the essentials of DAC systems—covering everything from their fundamental principles to key features that enhance security. We’ll explore effective strategies for developing access control policies and present best practices for successful implementation. Additionally, we’ll provide insight into measuring the results of your access control efforts, ensuring that your organization remains resilient against unauthorized access. Join us as we unpack everything you need to know about Discretionary Access Control Systems and prepare to elevate your security framework to new heights.
Understanding Discretionary Access Control Systems: Everything You Need to Know
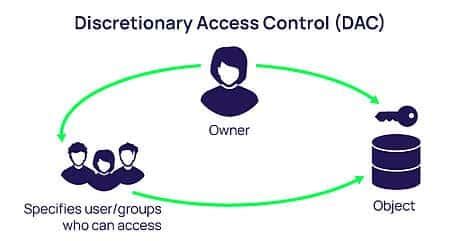
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) systems are a critical component of modern information security, enabling organizations to manage who has access to specific resources and data. In a DAC system, the owner of a resource has the authority to make decisions regarding access permissions. This flexibility allows for a collaborative environment while also necessitating a structured approach to privacy and security.
At the heart of Everything You need to know about DAC is its core principle of flexibility. Permissions can be granted or revoked easily, allowing resource owners to control access based on current requirements and contexts. Unlike Mandatory Access Control (MAC) systems, where access decisions are made based on fixed policies, DAC systems empower individual users.
One of the primary advantages of DAC systems is their alignment with the dynamic nature of organizations. Users often change roles and responsibilities, necessitating a swift adaptation of access rights. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining security without stifling productivity.
However, the discretionary nature of DAC also introduces challenges. A key concern is the risk of unauthorized access as users are granted permissions on a case-by-case basis. Without proper oversight, this can lead to potential security vulnerabilities. Therefore, organizations must implement stringent policies and regularly review access rights to ensure compliance and protection of sensitive data.
Understanding the balance between accessibility and security is paramount in leveraging DAC systems effectively. Organizations should invest in training and educate users about the importance of managing their own access rights responsibly. Overall, maintaining a robust framework around DAC can significantly enhance data security while supporting operational efficiency.
Key Features of Discretionary Access Controls: Inputs That Enhance Security
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) systems provide a flexible approach to managing access to resources, allowing users to control who can access their data. Here are some key features of DAC that enhance security:
- Owner Control: In DAC systems, resource owners have the authority to grant or revoke access rights to other users. This flexibility allows for tailored access based on the specific needs of individuals or groups.
- Granular Permissions: DAC allows for fine-grained permissions, enabling specific access levels for different users. For instance, users may be given read, write, or execute permissions based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Audit Trails: Many DAC systems include logging and auditing features, which track access to resources. This accountability enhances security by providing insights into who accessed data and when, allowing for the identification of potential security breaches.
- Dynamic Access Controls: Some advanced DAC implementations support dynamic access controls, which can adjust permissions based on factors like time of day, location, or user status, thus providing an added layer of security.
- Interoperability: DAC systems often support integration with other security mechanisms and protocols, allowing for seamless management of access across diverse systems and applications.
Focusing on these key features in your implementation can significantly enhance the security of your organization’s data while maintaining a balance between access and protection. In the context of everything you need to know about DAC, these features play a crucial role in ensuring that access controls are not only effective but also adaptable to changing security needs.
The Development of Access Control Policies: Steps to Build an Effective Framework
Developing robust access control policies is critical for ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information and systems. Here are the essential steps to build an effective framework:
By following these steps, organizations can develop a solid framework for access control policies that safeguards their resources while allowing for efficient operation. Remember, your goal is to have a well-structured access control system that ensures everything you need for security is effectively implemented.
Best Practices for Implementing Discretionary Access Controls Systems Successfully
When implementing Discretionary Access Controls (DAC), it is essential to follow specific best practices to ensure the system’s effectiveness and security. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Develop Comprehensive Policies: Establish clear access control policies that define user roles and permissions. Consider using a documented approach to maintain consistency and compliance.
- Utilize Least Privilege Principle: Grant users the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job functions. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Regularly Review Permissions: Conduct periodic audits of access permissions to ensure that they remain aligned with current user roles and responsibilities. Adjust access rights as needed when there are changes in personnel or job functions.
- Implement Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Utilize multi-factor authentication and other robust authentication methods to verify users’ identities before granting access to sensitive systems and data.
- Educate Users on Security Practices: Provide training to users on the importance of data security and how to recognize phishing attacks and other security threats. An informed user base is a critical line of defense against breaches.
- Monitor and Log Access Events: Continuously monitor user access and maintain logs of all access events. This will help you identify suspicious activity and respond to potential security incidents swiftly.
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Consider integrating RBAC within your DAC system to streamline permissions management, making it easier to assign and revoke access based on user roles.
- Regularly Update the DAC System: Keep your DAC software and policies up to date to address new security threats and vulnerabilities. Regular updates are vital for ensuring ongoing protection.
- Involve Stakeholders in Policy Development: Collaborate with various departments when developing access control policies to ensure that all relevant perspectives are taken into account.
- Test the System: Conduct penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify weaknesses in your DAC system. This can help you refine your access controls and enhance overall security.
By adhering to these best practices, you can significantly enhance the security and efficiency of your Everything You need to know about implementing Discretionary Access Controls systems, thus protecting sensitive information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Measuring the Results: Everything You Should Expect from Access Control Implementation
When implementing discretionary access control systems, it’s crucial to assess the outcomes effectively. Understanding how to measure results will help ensure that the Everything You need to optimize your security infrastructure is in place. Here are some key metrics to consider:
Implementing access control systems is an ongoing process. Regular reviews of these metrics will allow organizations to adapt their security measures continually, ensuring that they meet the dynamic needs of their environment while achieving the desired results from their discretionary access control implementations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Discretionary Access Control (DAC) systems?
Discretionary Access Control systems are security mechanisms that allow resource owners to determine who has access to their resources and what types of operations they can perform.
How do DAC systems differ from Mandatory Access Control (MAC) systems?
DAC systems enable owners to control access at their discretion, while MAC systems enforce access controls based on fixed policies established by the system administrator, often without input from resource owners.
What are some common applications of DAC systems?
DAC systems are commonly used in file systems, database management, and network security, enabling users to share files with specific individuals or groups based on their predefined permissions.
What are the potential risks associated with DAC systems?
The main risks include the potential for unauthorized access if resource owners poorly manage permissions, leading to data leaks or breaches.
Can DAC systems integrate with other security models?
Yes, DAC systems can be integrated with other security models, such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and MAC, to enhance overall security by combining the strengths of different approaches.
What are the key components of a DAC system?
Key components include user accounts, resource owners, access control lists (ACLs), and the specific permissions granted for various resources.
How can organizations effectively manage DAC policies?
Organizations can manage DAC policies by regularly auditing permissions, providing training for users on access rights, and implementing best practices for resource sharing and security management.