Explore Access Control Lists (ACLs) for enhanced security, management steps, real-world examples, and their benefits for data protection in this informative guide.
In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount, and one effective mechanism to achieve this is through Access Control Lists (ACLs). ACLs are essential tools that determine who is granted access to specific resources and what level of interaction they are allowed. By defining permissions within your systems, ACLs enhance security measures, prevent unauthorized access, and ultimately protect your valuable data. This article explores the fundamentals of Access Control Lists, shares practical steps for their implementation, and illustrates their real-world applications. We will also showcase the myriad benefits of employing ACLs in data protection, ensuring your organization stays ahead in the cybersecurity game. Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or just beginning to navigate the complexities of access management, understanding and utilizing Access Control Lists can significantly bolster your security framework.
Understanding Access Control Lists: A Key Concept
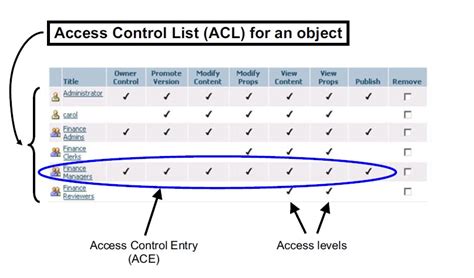
An access control list (ACL) is a fundamental component in the realm of computer security that dictates who can access specific resources and what actions they can perform on those resources. ACLs serve as a table of permissions associated with objects within a system, allowing administrators to define access rights for users and systems effectively.
At its core, an ACL consists of a list of permissions attached to a resource, which could be a file, directory, network device, or any other data type. Each entry within the ACL specifies a subject (user or group) and the operations (such as read, write, or execute) they are permitted to undertake. This granularity in permission management ensures that only authorized users gain access to sensitive information, reducing the risk of unauthorized disclosure or modification.
There are two primary types of ACLs:
- Discretionary Access Control Lists (DACLs): These lists grant permissions to specific users and groups, allowing resource owners to control access.
- System Access Control Lists (SACLs): SACLs are used for auditing purposes and track who accessed what and when, helping to maintain an audit trail.
Understanding the structure of an ACL is crucial for effective implementation. Below is a simple representation of how an ACL might appear for a file:
| User/Group | Permissions |
|---|---|
| Admin | Read, Write, Execute |
| User1 | Read, Write |
| User2 | Read |
In this example, the Admin has full control over the file, while User1 can read and modify it, and User2 can only read it. This structured approach not only enhances security by applying the principle of least privilege but also simplifies management and oversight of resource access.
How Access Control Lists Enhance Security Measures
Access Control Lists (ACLs) play a pivotal role in enhancing security measures within various systems. By defining who can access specific resources and what actions they can perform, access control becomes a streamlined process that mitigates unauthorized access risks.
One of the primary advantages of implementing ACLs is their granularity. ACLs allow administrators to assign permissions at various levels, from broad resource categories down to individual user permissions. This precision ensures that sensitive data is safeguarded and only accessible to authorized individuals, enhancing overall security posture.
Moreover, ACLs facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements. Many industries are mandated to protect personal and sensitive information, and having a clear structure of permissions helps organizations demonstrate accountability and adherence to these regulations.
Another significant aspect of ACLs is their ability to simplify audits and monitoring processes. By clearly outlining who has access to what, security audits can be performed efficiently, ensuring that user permissions align with organizational policies. This transparency aids in identifying any anomalies or potential security breaches swiftly, allowing for a proactive approach to threats.
Additionally, ACLs can be integrated with other security measures, such as authentication and encryption, to create a layered defense mechanism. This multi-faceted approach reinforces access control, making it considerably tougher for potential intruders to compromise security.
Utilizing Access Control Lists effectively strengthens an organization’s security framework. By enforcing specific permissions, supporting compliance efforts, facilitating audits, and integrating with other security strategies, ACLs are essential for maintaining robust access control measures in today’s digital landscape.
Implementing Access Control: Steps for Effective Management
Implementing access control is a critical process that involves multiple steps to ensure that resources are adequately protected while remaining accessible to authorized users. Below are the essential steps to effectively manage access control within an organization:
- Identify Resources: Begin by identifying all the resources that require protection, such as files, databases, applications, and physical facilities. Knowing what needs protection is the first step towards effective access control.
- Define User Roles: Clearly define the roles within your organization and the access levels associated with each role. This involves determining who needs access to specific resources based on their roles.
- Establish Access Policies: Create clearly outlined access control policies that dictate how resources can be accessed. This should include rules regarding who can access resources, under what conditions, and for what purpose.
- Implement Access Control Lists (ACLs): Utilize access control lists to specify which users or groups have access to each resource. This step is critical for enforcing your access policies effectively.
- Regularly Review and Update: Periodically review access control settings to ensure they remain relevant. Update ACLs and policies as necessary to reflect changes in user roles or resource availability.
- Monitor Access: Implement monitoring tools to track and log access requests to resources. This helps in identifying unauthorized access attempts and ensures compliance with access control policies.
- Train Employees: Conduct regular training sessions for employees to help them understand the importance of access control and the policies in place. Proper training ensures that everyone knows how to adhere to access protocols.
- Incorporate Automated Solutions: Where feasible, incorporate automated access control solutions that can streamline the management of permissions and enhance security measures.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively manage access control, therefore minimizing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Common Access Control List Examples in Real-World Applications
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are essential tools used across various platforms and environments to manage permissions and enhance security. Here are some common real-world applications where access control plays a crucial role:
- File Systems: ACLs are frequently used in operating systems like Windows and Linux. For example, in a Linux file system, each file and directory can have an ACL that specifies which users or groups have permission to read, write, or execute the file.
- Networking: Routers and switches often use ACLs to control traffic flow based on IP addresses, protocols, and port numbers. This allows network administrators to permit or deny specific types of traffic, improving overall network security.
- Database Security: Databases utilize ACLs to define who can read, write, and execute queries on the database. For instance, in SQL databases, roles can be assigned with specific permissions that regulate access to sensitive data.
- Web Applications: Many web apps implement ACLs to manage user permissions. For example, an e-commerce site might restrict access to admin functions, allowing only authorized users to manage inventory or process orders.
- Cloud Services: In cloud environments, such as AWS or Azure, ACLs help govern access to resources like storage buckets or virtual machines. These lists determine who can view or modify cloud resources, thereby protecting user data.
- IoT Devices: In Internet of Things (IoT) settings, ACLs are crucial for ensuring that only authorized devices and users can access control systems, which helps in protecting critical infrastructure from unauthorized access.
These examples illustrate the versatility of access control mechanisms in managing permissions and ensuring security across different technologies and environments. By implementing effective ACLs, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information and resources.
Benefits of Using Access Control Lists for Data Protection
Implementing access control policies through Access Control Lists (ACLs) provides several key benefits that enhance data security and management across various systems. Here are some notable advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Granular Control | ACLs allow for detailed permissions settings for individual users or groups, enabling precise control over who can access specific resources. |
| Improved Security | By restricting access based on roles and responsibilities, ACLs help mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. |
| Accountability | With ACLs, it is easier to track and audit user access, facilitating accountability and compliance with regulatory requirements. |
| Flexible Management | As organizational needs evolve, ACLs can be adjusted to quickly reflect changes in access requirements without complete system overhauls. |
| Reduced Risk of Human Error | Automating access rights through ACLs minimizes the likelihood of human error in permission settings, further enhancing security. |
Leveraging access control implementation through Access Control Lists not only helps organizations maintain a higher security posture but also fosters efficient management of data protection across diverse environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an access control list (ACL)?
An access control list (ACL) is a security feature that regulates who or what can access resources in a computing environment. It defines permissions for specific users or groups for a particular resource.
How does an access control list work?
An ACL works by specifying which subjects (users or system processes) can access which objects (files, directories, resources) and what operations they can perform (read, write, execute).
What are the components of an access control list?
The components of an ACL typically include the subject (user or group), the object (resource), and the permissions (read, write, delete, etc.) that specify what the subject can do with the object.
Can you give an example of an access control list?
Sure! For a file called ‘report.txt’, an ACL might specify that User A has read and write access, User B only has read access, and User C has no access at all.
What is the difference between a discretionary ACL (DACL) and a mandatory ACL (MACL)?
A discretionary ACL (DACL) allows users to control access to their resources at their discretion, while a mandatory access control list (MACL) enforces a policy that restricts access based on regulations that cannot be overridden by users.
How can access control lists improve security?
Access control lists improve security by allowing administrators to enforce specific permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data or resources, thus minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
What challenges might arise when managing access control lists?
Challenges in managing ACLs can include complexity in configuring permissions correctly, maintaining them over time as users and resources change, and ensuring that the policies align with the organization’s security policies.